Water is one of the most essential substances on Earth. From drinking and cooking to regulating the climate and supporting life, water plays an indispensable role in our daily lives. Despite its simplicity, many people are curious about its chemical name and the meaning behind it.
Knowing the chemical name of water not only satisfies curiosity but also provides insight into its molecular structure and unique properties that make it so vital for life.
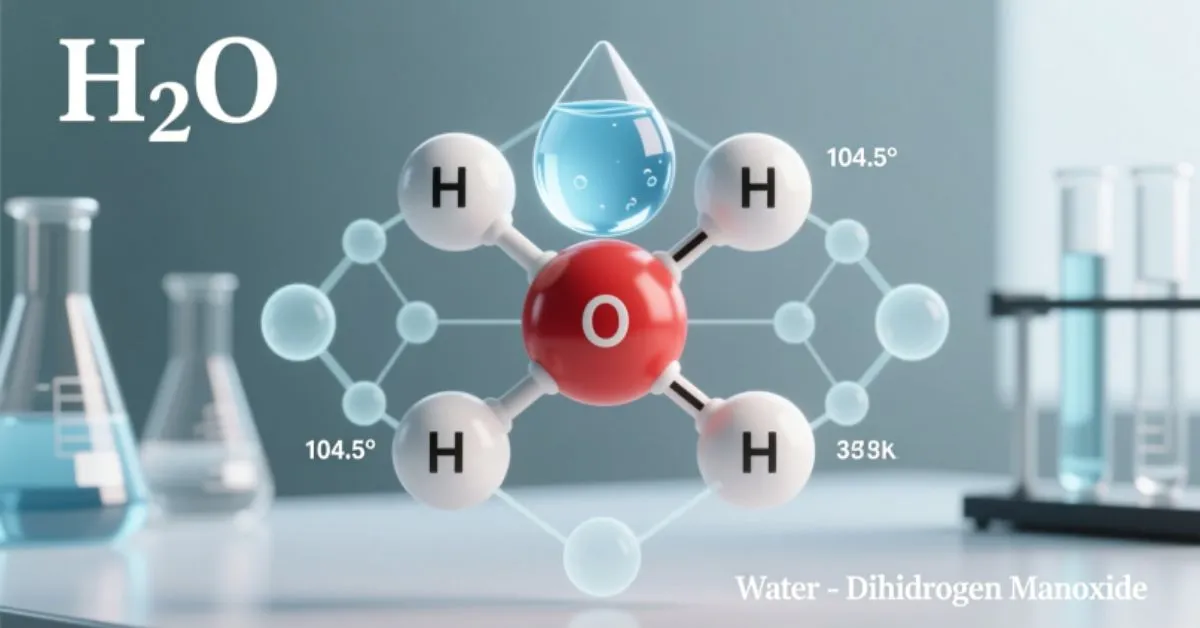
Quick Answer: The chemical name for water is dihydrogen monoxide (H₂O). This indicates that each water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Understanding this simple formula allows us to explore why water behaves as it does its high boiling and melting points, its ability to dissolve a variety of substances.
its critical role in biological and chemical processes.
What Is the Chemical Name for Water? 💡

Water is widely known by its everyday name, but its chemical name reveals its true molecular composition.
- H₂O: This is the molecular formula representing the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen in each water molecule.
- Dihydrogen monoxide: The systematic chemical name that describes its two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom.
Each molecule of water has two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to one oxygen atom. This simple yet elegant structure explains many of water’s unique traits, such as its polarity, hydrogen bonding, and ability to dissolve numerous substances.
Example: Sodium reacts with water to release hydrogen gas. This demonstrates the molecule’s reactivity and why understanding H₂O at the chemical level is important.
In short: Water = H₂O = Dihydrogen Monoxide.
History of Water’s Chemical Name 🧪
Water has fascinated scientists for centuries. In the 18th century, chemists began exploring its chemical composition:
- 1781: Henry Cavendish identified hydrogen as a component of water.
- 1783: Antoine Lavoisier proposed that water is a combination of hydrogen and oxygen, forming H₂O.
- 1790s: The term dihydrogen monoxide was formalized to describe water chemically.
This discovery helped scientists understand the molecule’s behavior in reactions, such as combustion and acid-base interactions, paving the way for modern chemistry.
Structure of Water Molecule 🧬
Water’s structure is fundamental to its unique properties:
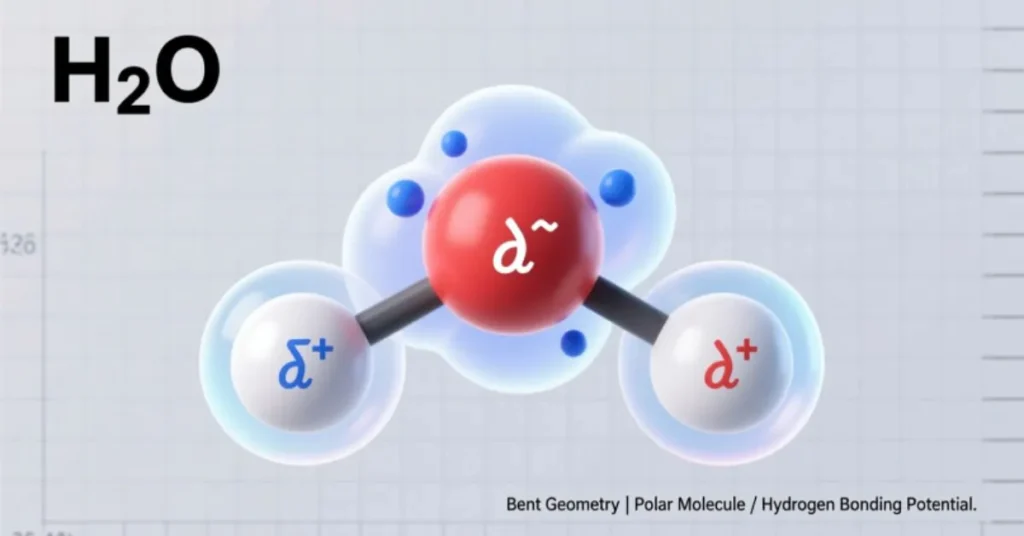
- Bent molecular shape: The angle between the two hydrogen atoms is approximately 104.5°.
- Polar molecule: Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, creating a partial negative charge on oxygen and partial positive charges on hydrogen.
- Hydrogen bonding: These bonds between water molecules lead to high surface tension, cohesion, and adhesion.
This structure explains why water is such a universal solvent and why ice floats, maintaining life in cold environments.
Physical Properties of Water 🌡️
Water’s chemical composition influences its physical characteristics:
- Boiling point: 100°C (212°F) at standard pressure
- Freezing point: 0°C (32°F)
- Density: 1 g/cm³ at 4°C
- High heat capacity: Water absorbs and releases heat slowly, stabilizing Earth’s climate.
These properties make water crucial for sustaining life and regulating ecosystems.
Chemical Properties of Water ⚗️
Water participates in a wide range of chemical reactions:
- Acid-base reactions: Acts as both an acid (H⁺ donor) and base (OH⁻ donor).
- Hydrolysis: Breaks chemical bonds in larger molecules, like proteins and carbohydrates.
- Redox reactions: Can act as an oxidizing or reducing agent in chemical processes.
Example: Water reacts with sodium to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
This chemical versatility is why H₂O is central to many industrial, laboratory, and biological processes.
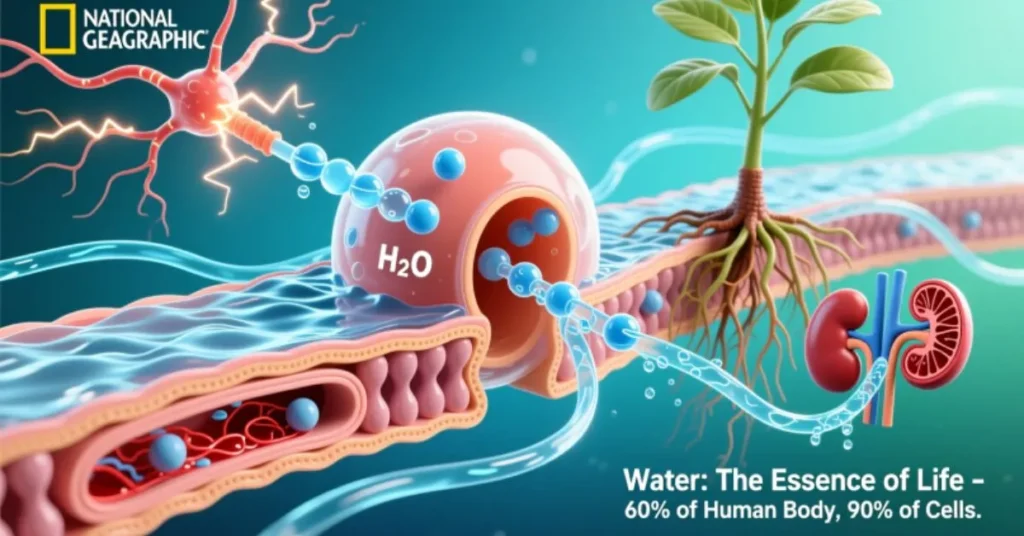
Biological Importance of Water 🌱
Water is life’s cornerstone:
- Makes up 70% of the human body
- Serves as a solvent for nutrients and waste products
- Regulates body temperature through sweating and respiration
- Participates in photosynthesis, forming the basis of life on Earth
Without water, life as we know it could not exist. Its chemical composition directly supports these essential biological functions.
Water as a Universal Solvent 🧴
Water’s polarity allows it to dissolve a vast array of substances:
- Salts like NaCl dissolve easily because ions interact with water molecules
- Sugars dissolve due to hydrogen bonding
- Gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide can dissolve, supporting aquatic life
This property makes water the “universal solvent,” essential for chemical reactions in both nature and laboratories.
Industrial Uses of Water 🏭
Water is crucial in industries due to its chemical properties:
- Cooling agent in power plants
- Solvent in chemical manufacturing
- Transport medium in pipelines
- Cleaning and sanitation in food and pharmaceutical industries
Its simple chemical formula hides the complexity of its industrial applications.
Environmental Importance of Water 🌍

Water’s chemical and physical properties also protect the environment:
- Maintains aquatic ecosystems
- Supports plant growth through hydration
- Regulates climate through evaporation and precipitation
- Forms glacial and river systems, shaping landscapes
Understanding its chemical composition helps scientists address water pollution and conservation.
Fun Facts About Water 💦
Water is not just essential but fascinating:
- Covers 71% of Earth’s surface
- Exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas
- Expands when frozen, making ice less dense than liquid water
- Can form over a million hydrogen bonds in a small volume
- Participates in biochemical reactions vital for life
These facts highlight the significance of water beyond its everyday use.
Conclusion
Water, or dihydrogen monoxide (H₂O), is a simple yet extraordinary molecule. Its chemical composition explains its physical and chemical properties, biological importance, and role in industrial and environmental systems.
From supporting life to shaping landscapes, water is truly essential. Understanding its chemical name allows us to appreciate the science behind this vital substance and its countless applications. Next time you take a sip of water, remember the tiny H₂O molecules working silently to sustain life.